We republish in two parts an investigation first published by In-depth Solomons and undertaken in collaboration with the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP).
A decade ago, torrential rains flooded Honiara, the capital of Solomon Islands, overwhelming its decrepit water treatment system. Over a dozen people were killed and thousands more stricken with diarrheal disease.
The state-owned water and sewage company, Solomon Water, quickly developed a plan to improve clean water production and distribution in the capital and elsewhere. By 2019, the utility had secured more than US$90 million in loans and grants for the project, primarily from the Asian Development Bank (ADB), one of the largest sources of development funding in the Asia-Pacific region.
Nearly US$20 million was budgeted for the plan’s centerpiece, the Kongulai Water Treatment Plant, which was intended to provide more than 15 million litres of clean water daily to the people of Honiara starting in 2023. But today, not a single drop of concrete has been poured, and barely any of the money earmarked for the project has been spent. Outbreaks of waterborne diseases, meanwhile, are as common as ever in the capital’s increasingly crowded districts.
The project ran aground after it was granted to its lowest bidder: an Indian joint venture that repeatedly missed deadlines, failed to carry out planned work, and was even in the process of being blacklisted by an Indian state for failing to complete other ADB-backed projects while its Solomon Islands bid was under evaluation.
Solomon Water officials repeatedly expressed concerns about the joint venture — composed of two Indian contractors, Rean Watertech and P.C. Snehal Ltd — and raised questions about its bid, records obtained by OCCRP and its partner In-depth Solomons show. According to three people involved in the project, the ADB dismissed these objections and pushed the utility to accept the bid.
Meanwhile, a company owned by the son of Mines, Energy, and Rural Electrification Minister Bradley Tovosia — the official with ultimate authority over the Kongulai project — was hired by the Indian joint venture to carry out the only minor works that have been completed so far. Tovosia did not declare the work to parliament.
Reached by reporters, he dismissed his son’s involvement in the project as a “small issue,” and promised to respond the next day, but never did. His son said he was never paid for the work.
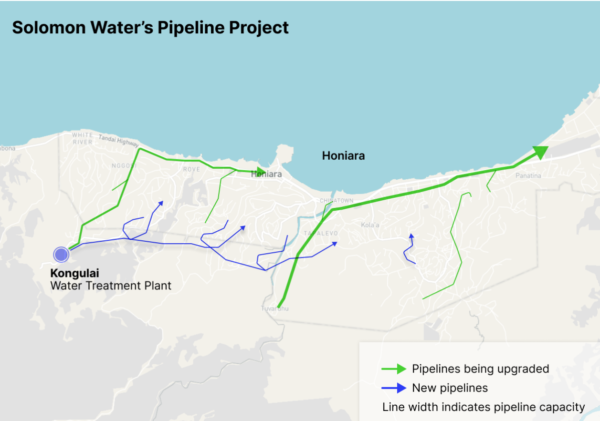
Figure 1: Solomon Water’s plan to expand and upgrade its clean water services in Honiara
Credit: Edin Pašovic, OCCRP/Solomon Water
Our investigation was based on a review of tens of thousands of documents and emails leaked to In-depth Solomons and shared with OCCRP, covering the project’s early planning stages in 2018 through this summer. Reporters also spoke with five people with detailed knowledge of the project, most of whom asked not to be identified due to fears of losing their jobs or being frozen out of future ADB work.
The acceptance of the Rean/PCS bid despite the concerns expressed by Solomon Water officials is symptomatic of development projects throughout the Pacific, Terence Wood, a fellow at the Australian National University’s Development Policy Centre, said.
“There is a tendency amongst all aid donors — the ADB included — not to listen sufficiently to stakeholders when working in the Pacific. At its worst, failures of this sort can mean lives lost — the lives of people that would have been saved if the project had worked.”
ADB declined to answer specific questions about the project or why it was awarded to the Indian joint venture, but said that “Rean Watertech/P.C. Snehal LTD is not debarred by ADB, hence this company is eligible to participate in ADB-financed projects and activities”.
Rean Watertech and P.C. Snehal did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
The Kongulai plant was intended to sit in a water catchment nestled in the thickly forested hills overlooking Iron Bottom Sound, named for the dozens of ships and planes that were sunk there during the Second World War.
In late 2021, Rean/PCS put in a bid for US$15.6 million to build the plant, tender documents show. This was nearly US$5 million lower than its nearest competitor, an Australian company with a record of working in Solomon Islands, and 20% cheaper than Solomon Water’s own US$19.6 million estimate.
Staff at the utility worried the offer was too good to be true. An early version of the bid evaluation report — a technical review prepared by Solomon Water officials for the ADB — shows the utility expressing concerns that US$15.6 million would not even cover the necessary equipment and materials.
The authors of the evaluation, which was submitted to the ADB procurement team in January 2022, also noted that the bid lacked details in key sections describing the actual work to be done. That led the authors to question whether the Indian venture understood what completing the project would entail.
“Due to not directly answering or addressing items called for in the technical evaluation some questions do exist on how this substantive project will be delivered on a tight timeframe,” the report noted. “Poor understanding of standard safeguards management and practices on donor funded projects is exhibited.”
The report also noted that the proposed pricing “presents a serious risk to [Solomon Water] of poor quality mechanical plant delivery and significant cost over-run during operations.”
At the same time, the report noted, the Rean/PCS budget had priced water purification chemicals, to be used during the plant’s operation, at “exceptionally high rates”. The authors said they feared the joint venture might try to recoup losses incurred during construction by using those chemicals at a “higher than expected” pace in the project’s first year.
The report recommended the bid be rejected.
But according to three people involved in the project, ADB dismissed the concerns, pointing out that another company had bid even less than Rean/PCS but had been rejected due to a lack of experience.
The next version of the report, sent to ADB staff two weeks later, insisted that Rean/PCS address the Solomon Water officials’ concerns before the bid would be accepted. But this line did not appear in later versions of the report, and the version ultimately approved by the ADB recommended that the contract go to Rean/PCS.
Former Solomon Water CEO Ian Gooden said that the changes were made to subsequent versions under pressure from the ADB. “We did not want to award the contract,” Gooden told OCCRP, but the ADB “required that we proceed”.
“I think it was simply: ‘This is the cheapest bid. You have to take the cheapest bid.’”
Two others involved in the project, both of whom asked not to be named to protect their jobs, said they shared this interpretation and felt pressured by the ADB to accept the Rean/PCS bid despite their concerns. The ADB did not respond to specific questions about the reports.
In part 2 of this blog, the authors will describe what happened following the acceptance of the Rean/PCS bid.





Keep up the good work, guys. Exposing the truth is an uphill undertaking but remember the truth always prevails no matter what. Just don’t give up.
Thank you, In-depth Solomons as you continue uncover corruption, fraud, mismanagement, nepotism and injustice. Tell the truth to power.
Good report, wantoks. The ADB is corrupt to the core. The MPs’ family being involved in the project is no small matter. Wonder why nothing of benefit to is being seen in Honiara. The people should not accept this kind of direct pressure being imposed by the minister on technical people to accept a substandard quote.